The financial world is changing, and it is not the same as it was yesterday, so yes, we could say that it is changing every day. On one hand, technology has allowed banks to process millions of transactions every day at lightning speed; on the other, it has exposed them to various fraud risks, which is why banks need fraud detection tools. Synthetic identity fraud and phishing scams mean that fraudsters are using various tactics and technologies to bypass banking systems and their security measures just to profit. For banks, it is a lot more than just a financial issue. It is a matter of trust as well.
AI is powerful against fraud. Its ability to learn from data, identify patterns, and make real-time decisions allows financial institutions to keep user accounts secure.
Why Traditional Systems No Longer Work
Traditional fraud detection methods almost always rely heavily on rules and manual processes, like:
- Transactions over a certain amount might trigger alerts.
- Transfers from specific locations could also be alerted to the team.
- Known blacklisted accounts or IPs are automatically blocked.
Well, yes, you can say that these rules offer protection against fraud, but it is not as effective as AI could be, because these traditional rules almost always run short when fraudsters decide to change their tactics.
The thing with these traditional methods is that they can not adapt in real-time, which often results in a high number of false positives, and they can not keep up with the volume of today’s digital banking activity.
Consider The Implementation of AI
If you are still using traditional systems as your primary security for the bank, well, we hate to break it to you, but the bank could be in real danger. AI brings something that traditional systems lack: adaptability.
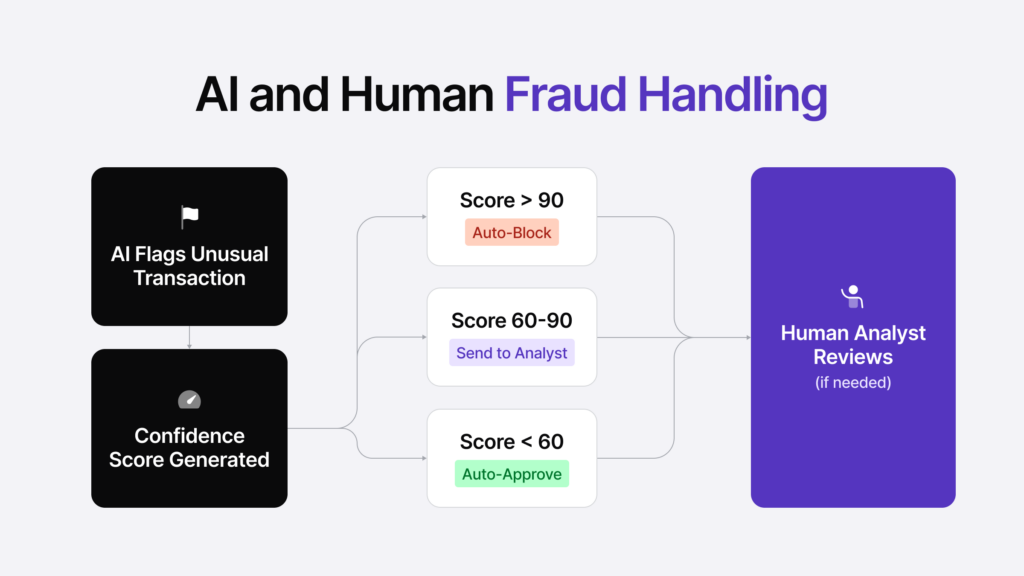
Instead of depending on predefined rules, AI systems learn what constitutes “normal” behavior and continuously update their understanding as new data comes in. When something deviates from the norm, the system flags it, and then the human agent takes over for the investigation of the issue that occurred.
AI does this:
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI can analyze thousands and thousands of transactions in minutes, and if any unusual activity or transaction occurs, it instantly gets alerted to the human team.
- Pattern Recognition: Machine learning models can identify simple and complex patterns that humans or traditional software would just simply miss.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI systems track user behavior, such as login patterns and device usage. Additionally, mouse movement and typing speed can also be monitored. Sudden changes could indicate fraud.

Main Technologies That Are Used in Fraud Detection (AI)
There is not just one type of AI. Several technologies work together to make fraud detection way smarter and faster:
- Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms can learn from historical data, which makes it perfect for learning new fraud tactics. The more data they analyze, the better they become at identifying fraudulent patterns. This can include the following: unusual transaction locations, transactions themselves, timings, or merchant categories.
- Deep Learning (DL): Deep Learning works together closely with ML, taking it further using the network to simulate human-like decision-making. It is really effective at analyzing sequences of transactions and flagging unusual patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP, on the other hand, allows AI systems to read and interpret unstructured data, emails, and chat logs, which helps to identify phishing attempts.
- Anomaly Detection Algorithms: These algorithms do not need labeled data to function because they monitor for outliers and unusual behaviors.
- Behavioral Biometrics: AI can establish behavioral baselines, and any deviation might trigger an alert, even if it coincides with a low-risk transaction.
Benefits for Banks and Users
If you thought that AI only does safety things, well, you are right, but it also does more than that – it gives benefits for banks and their users as well. Let’s talk about it.
- Reduced False Alarms: Users are less likely to have their legitimate transactions blocked, avoiding any inconveniences.
- Faster Resolution: When fraud is detected accurately and quickly, it is better for both the bank and users. Affected users get quicker resolution and compensation.
- Efficiency for Operations: AI can automate tasks previously handled by analysts, allowing teams to focus on more complex tasks.
- Cost Savings: Less fraud means fewer chargebacks and lower operational costs.

Ethical Concerns
Of course, the integration of AI is fun and all, but it also comes with its flaws.
Data Privacy: As we all know, AI systems need a lot of data to function effectively. Ensuring that this data is collected, stored, and processed in a way that complies with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is important.
Bias and Fairness: If historical data contains biases (e.g., targeting certain demographics unfairly), in this way, the AI could unfairly benefit the organization.
Explainability: One major criticism that AI gets, especially deep learning models, is their “black box” nature. Regulators and users want to know why a specific decision was made – and that is not always easy to answer.
Fraudster Evolution: The irony is that criminals are using AI themselves to make better attacks, leading everybody to the technological arms race, so as AI gets smarter, so do criminals.
The Future
AI is just getting started in the banking sector, but various forecasts are available, and in the next few years, we are likely to see these innovations:
Federated Learning: Allows banks to collaborate and train shared models without risking sensitive user data.
Explainable AI (XAI): New tools are being created to make AI decisions more transparent.
Deeper Integration With Blockchain: Smart contracts could automate security checks and make fraud nearly impossible.
Collaboration Across Institutions: With AI, various platforms that share anonymized fraud data to improve the defense against fraud collectively.
Conclusion
Fraud detection was always about catching the bad guys after the fact, but now it is just not the case. Banks, for example, can now predict and prevent fraud, protect data, and secure user accounts. As time goes by, fraud tactics and AI capabilities continue to improve, and staying ahead will require constant innovation and collaboration.




