It’s clear that the world has a money laundering issue. And despite regulators’ efforts to prevent financial crime, this task remains challenging. Especially because a significant portion of money laundering activities remains concealed. This complexity comes not only from the ongoing efforts of law enforcement but a combination of many factors, including geographical influences or socio-economic factors, such as less-regulated regimes or the rise of extensive criminal networks.
Recent data indicates that in the UK, money laundering stands out as the most common Anti-Money Laundering (AML) event, with AML compliance failures following closely behind. The process of money laundering, known as “washing,” consists of moving money through various financial institutions via transfers until it appears legitimate. This nefarious practice that has extended beyond national borders in many countries remains a problem for the global economy. It’s also a serious hassle on a more local level and a headache for many regulated businesses.
In this context, AML rules play a crucial role. More importantly, automated tools, such as AML software turn compliance into a smooth, more efficient ongoing process that ticks all the right boxes, including helping companies detect and report suspicious activity in terms of safeguarding from predicate offenses like money laundering and terrorist financing.
What Does AML Mean?
AML, short for Anti-Money Laundering, is a globally recognized term that represents efforts to combat and prevent financial crimes associated with illicit money activities. It consists of actions undertaken by financial institutions and other obliged entities to comply with legal requirements, involving the proactive monitoring and reporting of suspicious activities.
AML rules, together with Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) policies, are vital measures that address crimes like terrorist financing, human trafficking, drug dealing, fraud, and other illicit activities. AML regulations integrate the scrutiny of money laundering (the source of funds) and terrorism financing (the destination of funds).
Countries and international bodies, like the European Union (EU), mandate strict AML programs for relevant companies in sectors like fintech, banking, payment processors, insurance, gambling, crypto, real estate, and more.
The FATF and its Role in AML Compliance
Financial sector regulators worldwide adhere to the guidelines of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) to combat money laundering. The FATF is a global regulatory body guiding companies in addressing money laundering and terrorism financing.
Through its 40 Recommendations, it expects member jurisdictions to adopt a unified AML/CFT approach, enabling regulated entities to establish robust anti-money laundering programs and contribute to the fight against fraud and financial crime.
FATF’s 40 recommendations guide companies to maintain robust AML practices by following these steps:
- Identify financial crime. Recognize various types of financial crime threats within a country’s existing policies and systems.
- Implement anti-fraud policies. Develop and enforce policies and procedures in the country’s financial infrastructure to counter identified threats like money laundering, terrorist financing, drug trafficking, and weapon trading.
- Build a proper AML program. Establish preventive measures for financial institutions and reporting entities aligned with FATF’s AML and CFT recommendations. These measures encompass record-keeping, transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, and AML screening.
- Collaborate with law enforcement. Empower the country’s law enforcement entity with the authority to enforce laws, oversee reporting entities, and implement risk prevention measures.
- Practice accountability. Foster accountability at all levels within the system and maintain a fair judiciary in the country.
FATF issues guidance to align international standards and advise countries on the most effective methods to prevent illegal activities. Due to the dynamic nature of financial crime, FATF consistently updates and revises its recommendations.
What is the Meaning of AML in Software?
AML software refers to an automated tool used in the financial and related sectors. It helps various companies meet compliance demands as well as prevent, detect, investigate, and report suspicious activities associated with money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud.
Positioned at the core of an organization’s compliance efforts, AML software plays a pivotal role for most companies, especially those that are handling a high volume of daily transactions from all around the world. Proper AML software is able to screen transactions in real-time and offer detailed insights to examine customers and transaction history while identifying certain AML red flags and suspicious behavior.
How Does AML Software Work?
AML software works by tracking transactions and analyzing suspicious activity while later if needed, generating Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) to follow and identify parties involved. It also frequently scans and maintains a database of countries to identify clients on a regulatory body’s blacklist. In AML compliance, a blacklist occurs when the FATF deems a country as not meeting its standards for preventing financial crimes, such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing, and when there are no significant efforts to address these issues.

AML software has two key goals, which oblige companies to:
- Follow FATF’s recommended risk-based approach. For high-risk customers like politically exposed persons (PEPs), organizations should implement enhanced due diligence (EDD) measures for stricter monitoring as well as to detect changes in customer risk levels.
- Ongoing compliance with KYC, also known as Perpetual KYC (pKYC). This is when the AML software adopts a proactive approach by continuously monitoring customer behavior. Using the software, the company can receive automated alerts triggered based on customer behavior and replace many manual compliance tasks, such as risk assessments.
This way, AML software assists institutions in fulfilling daily AML compliance requirements and staying vigilant to emerging hazards.
Related: How Can RegTech Improve AML Compliance?
What Features Should Effective AML Software Have?
Effective AML software must have the capability to identify suspicious transactions. Most AML screening and ongoing monitoring solutions use artificial intelligence, which helps enhance and streamline the process of transaction monitoring. So, when assessing AML software, companies should prioritize features that align with both global and local AML regulatory standards, as well as industry-specific regulations.
A robust AML software will always be able to help companies complete these AML tasks:
- Perform identity verification checks
- Conduct customer due diligence (CDD)
- Identify and monitor changes in ultimate beneficial owners (UBO)
- Screen customers against PEPs and sanctions lists
- Facilitate automated screening and monitoring for adverse media
- Assess and update the level of financial crime risk
- Monitor transactions and report suspicious activities
- Retain records of the company’s due diligence efforts
Moreover, the software should be able to integrate data from third-party sources, including government-compiled databases. For compliance with suspicious activity report (SAR) requirements, the AML software should collect and present accurate and up-to-date data, aiding in the preparation and submission of electronic reports. That’s because robust AML software should support detailed reporting to offer regulators a credible overview of the company’s compliance efforts.
Related: Streamlined AML Compliance 101 for Businesses
Types of AML Software
AML software assists companies in achieving AML compliance, typically focusing on three aspects: customer screening, transaction screening, and ongoing monitoring. However, there are various types of AML software that can be used to automate compliance processes.
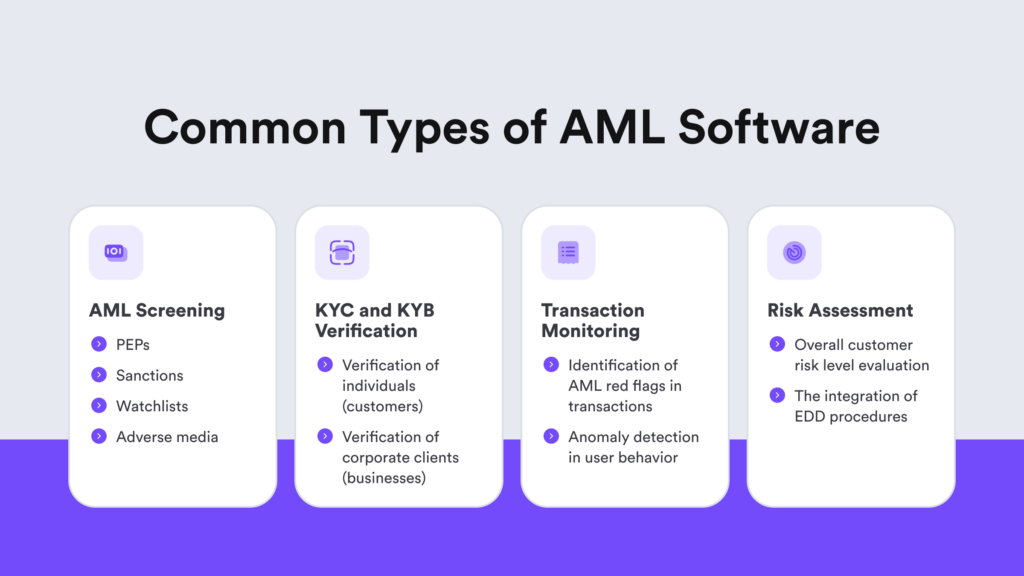
These include:
1. AML Screening
This type of AML software screens individuals or entities on sanctions, PEPs, watchlists, and other global wanted lists. These groups are considered high-risk customers and have their own lists due to an elevated risk of money laundering and potential links to financial crimes like bribery and corruption. Automated AML screening software maintains a high-risk database for money laundering and financial crimes, comparing new customer or transaction data to alert users of any matches.
In essence, financial institutions and regulated industries use AML screening software on customers to:
- Assess their risk level.
- Avoid engaging with risky individuals, such as sanctioned entities and PEPs.
In general, AML screening is an integral process to a comprehensive AML program. It works alongside transaction monitoring, risk management, and reporting suspicious activities. Beyond compliance, screening safeguards businesses from becoming conduits for evolving financial crimes. Factors like virtual asset providers and cryptocurrencies introduce new challenges with increased anonymity and speed in fund transfers.
2. KYC and KYB Verification
KYC/KYB software verifies the identity of individuals and businesses. In general, KYC software checks transactions with individuals, while KYB focuses on maintaining trusted relationships with corporate customers, often also referred to as corporate KYC. The interconnection between KYB and KYC is inherent, as KYC is another part of the KYB process.
The KYC and KYB verification software typically incorporates tools for collecting and verifying customer information, including name, address, date of birth, and government-issued identification. The gathered data is then used to identify and flag high-risk customers and suspicious transactions.
KYC verification is typically initiated during customer onboarding and persists throughout the entire business relationship. In the meantime, KYB verification extends to confirming the identities of individuals linked to the screened companies. This involves gathering and verifying information, such as government reports, tax records, or financial statements, to assess the legitimacy of businesses seeking services. When choosing a proper AML software, companies should look for a tool that carries both KYC and AML verification features in order to stay compliant.
Related: KYB vs KYC — What is the Difference?
3. Transaction Monitoring
Automated transaction monitoring software can screen and review transactions in real-time. It flags suspicious transactions that potentially indicate financial crimes, such as money laundering.
Transaction monitoring software assists companies in achieving these AML-related tasks:
- Establishing the customer’s risk profile
- Conducting ongoing monitoring
- Detecting anomalies
- Investigating specific suspicious activity
- Reporting such activity to the authorities
Typically, it uses AI and machine learning, which are able to use custom rules to analyze transaction data, identifying patterns or anomalies associated with money laundering. What’s best is that AML software allows companies to create rules and integrate pre-built transaction monitoring rules.
Custom Rules in AML Software for Detecting Anomalies
Certain red flags can be customized to trigger an automated alert when using AML software. For example, if the company faces these scenarios:
- An abnormally high transaction, which is atypical for the client
- A sudden profile change before a large transaction
- Multiple high-volume transactions from a recently onboarded user
- An unexplained pattern in customer behavior that raises suspicion
- Activity from a different geographical location than the customer’s typical address
- A suspicion of potential structuring in money laundering because of split transactions
- A repeated value or pattern for round-sum transactions
- Unusual client activity outside normal business hours
- A high increase in the general transaction volume
4. Risk Assessment
This type of software analyzes the risk of money laundering and financial crimes based on the company and its customers. It’s part of an organization’s ongoing compliance efforts that are designed to ensure proper risk management and periodic reviews. This also involves key risk indicator monitoring and updating risk mitigation measures, such as implementing additional AML controls or conducting EDD.
In other words, AML software uses built-in risk assessment tools to identify and automatically check potential risks linked to customers, products, services, and transactions. Some advanced features for AML risk assessment typically include assigning risk scores for customers and entities based on factors like customer type, location, PEPs and sanctions screening.
AML software enables companies to maintain a current and precise risk assessment strategy through the following steps:
- Helping develop a robust AMLprogram for minimizing the risk of money laundering.
- Using automation, applying a risk-based approach to detect and prevent money laundering.
- Providing necessary data to understand the risk level associated with each customer.
- Detecting and mitigating various risk sources.
Regularly updating customer information, including occupation, industry, address, and externally sourced details like adverse media, is crucial for accurate risk assessments. That’s why automated risk assessment using AML software should rely on real-time updates of risk profiles through continuous monitoring activities.
Why is AML Important?
It’s no secret that fraudsters often employ money laundering techniques to conceal their illegal gains, posing challenges to detection and prevention. AML is important because it extends beyond safeguarding the financial system from illicit activities.

In addition to the moral obligation to combat money laundering and terrorist financing, companies use AML software for several reasons, such as shareholder value and reputation guarantees or better risk mitigation and cost reduction.
Consequences of Non-Compliance in terms of AML
Consequences for getting involved with money laundering, including criminal liability for individuals within the company, are serious. Companies investigated or fined for non-compliance can lose customer trust, with financial corruption charges attracting negative media attention.
Some of the most notorious examples of fines regarding non-compliance with anti-money laundering measures include:
- Deutsche Bank was fined $630 million in 2017 for AML failures related to Danske Bank for a major money laundering scandal.
- JPMorgan Chase had to deal with a $1.7 billion fine in 2014 for AML failures linked to the Bernie Madoff Ponzi scheme.
- HSBC incurred a $1.9 billion fine back in 2012 due to non-compliance for helping Mexican drug cartels to launder money.
Additionally, poor customer experience is a consequence of AML non-compliance, increasing the risk of fraud and negatively impacting customers in the event of a successful attack. That’s why choosing the right AML compliance software is vital, as some may not meet customer expectations for efficiency and security in terms of safeguarding their finances.
Advanced Risk Mitigation with iDenfy’s AML Software
iDenfy has built a single AML software that carries multiple features helping regulated businesses from different industries shape their AML programs through custom rules and all the needed tools in one place, including:
- Identity verification (KYC — document verification, selfie verification, and more)
- Business verification (KYB — corporate entity onboarding with multiple customization options, such as automated credit bureau reports or collected shareholder data)
- Transaction monitoring (premade SAR blueprints, additional KYC verification generation, built-in ongoing AML screening, and custom rules based on set thresholds)
- Anti-fraud and risk profiling tools (fraud scoring, IP address analysis, and more)
- An easy-to-understand dashboard with audit trails for straightforward use by internal compliance teams.
- While labeling options to match your brand identity.
If needed, you can also check our latest breakdown of the best AML software providers for further due diligence.
Don’t hesitate. Get started right away.




